
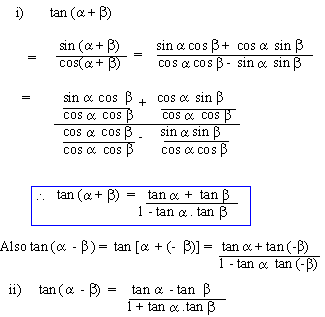
There are few inverse trigonometric functions. Sec a = 1/ (cos a) = Hypotenuse/Adjacent = CA/AB The sum identity for tangent is derived as follows: To determine the difference identity for tangent, use the fact that tan() tan. Further, tan can be written in terms of sine and cos as Tan a = sina/cosa.Īdditional functions are represented through formulas they are:Ĭot a = 1/ (tan a) = Adjacent/Opposite = BA/CBĬosec a = 1/ (sin a) = Hypotenuse/Opposite = CA/CB Formulas for the tangent function can be derived from similar formulas involving the sine and cosine.
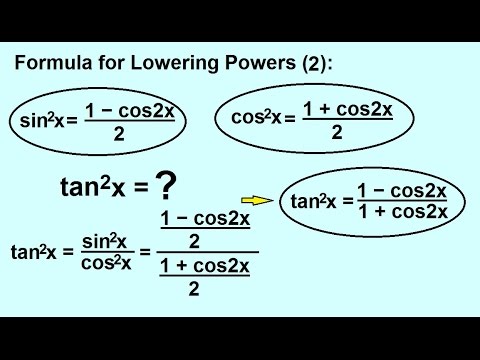
Hence, the tan function will be derived as Tan a = Opposite/Adjacent = CB/BA. Tan 3x 3tanx-tan3x/ 1-3tan2x Trigonometry formulas for class 10, 11 and 12. The student should note that the tan function can be exhibited in terms of sine and cos as their ratio. The tan function formula is defined as the ratio of the length of the opposite side of the right-angled triangle to that of the adjacent side. The cos function can be derived from the above reference diagram as
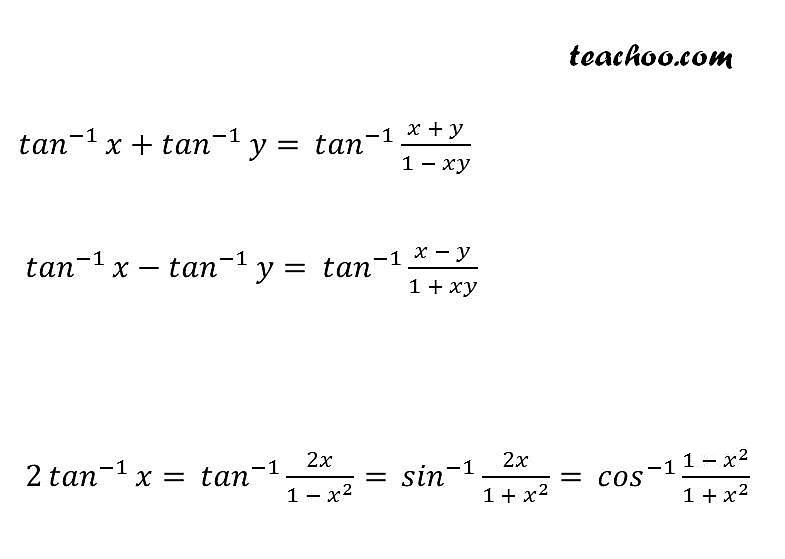
The cos function formula can be explained as the ratio of the length of the adjacent side to the length of hypotenuse. The sin value should be Sin a= Opposite/Hypotenuse=CB/CA. The ratio between the length of an opposite side to that of the hypotenuse is known as, the sine function of an angle. The formula for some trigonometric functions is given below. It should be noted that the reciprocal of tan, cos, and sin are known as cotangent (cot), secant (sec), and cosecant (csc), respectively. These functions are also established from the primary functions, like sine, cos and tan. List of additional trigonometric functions include secant, cosecant, and cotangent. The above diagram can explain the three trigonometric primary functions.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
